TRON

longjames
2023-11-24 14:55
Investing in Tron was a great decision. The community and development team are both top-notch.

Neutral

Pius O
2023-11-11 02:59
I consider TRON cryptocurrency as one of the best in the world.

Neutral
SolNFT
2023-10-31 07:41
Tron (TRX) is a blockchain platform and cryptocurrency that aims to create a decentralized internet

Positive

daniez
2023-07-26 09:00
Tron is one of my favourite coin

Positive

Ngwu
2023-07-26 08:59
God bless Tron

Positive

deesucre
2023-07-26 08:50
Tron is cool, been enjoying it.

Positive

0xmar1a
2023-01-15 23:11
very amazing token!

Positive
Overview of TRON
TRON is a decentralized digital platform based on blockchain technology. It was established in September 2017 by a Singapore-based non-profit organization named the TRON Foundation. The foundation was headed by CEO Justin Sun, a notable web entrepreneur and former representative of Ripple. TRON aims to build a free, global digital content entertainment system with distributed storage technology, allowing easy and cost-effective sharing of digital content.
The TRON network uses its cryptocurrency, TRONIX (TRX), for transactions within this ecosystem. It is designed to support the construction of a decentralized Internet and some of its assumed advantages include high throughput, high scalability, and high availability for all Decentralized Applications (DApps) in the TRON ecosystem.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| High throughput | Accusations of plagiarism in code |
| High scalability | Lack of fully decentralized model |
| High availability for DApps | Controversial marketing strategies by the founder |
| Supports construction of a decentralized Internet | Adoption and real-world application challenges |
| Cost-effective sharing of digital content |
Pros:
1. High throughput: One of the key characteristics of TRON is its high throughput, which essentially means that it has the capacity to process numerous transactions per second. Higher throughput leads to faster processing and lesser delays in the blockchain network.
2. High scalability: The nature of TRON's architecture allows it to readily scale and handle the increasing amount of work or its potential to be enlarged to accommodate that growth. It contributes to the network's overall efficiency and functionality.
3. High availability for DApps: Decentralized applications (DApps) play a substantial role in blockchain ecosystems. TRON prides itself on its high availability for DApps, meaning developers can create and users can interact with DApps readily on the TRON network.
4. Supports construction of a decentralized Internet: TRON's objective is to support and advance the decentralization of the Internet. This means a shift away from regulated, server-based networks towards peer-to-peer systems.
5. Cost-effective sharing of digital content: By leveraging blockchain and peer-to-peer (P2P) network technology, TRON enables creators of digital content to cut out middlemen such as the Apple Store and Google Play Store. This fosters direct consumer-to-creator transactions, reducing costs and improving content availability.
Cons:
1. Accusations of plagiarism in code: TRON has been accused of violating licensing agreements because large portions of its code were allegedly taken from EthereumJ, a project from Ethereum. Though these allegations have been addressed, they have posed questions about the project's originality and integrity.
2. Lack of fully decentralized model: Although TRON aims to facilitate a decentralized Internet, its Super Representative governance system has been critiqued for potentially creating centralization within the network, contradicting its own principles.
3. Controversial marketing strategies by the founder: The TRON founder, Justin Sun, has attracted controversy and criticism for some of his promotional tactics. His strategies include aggressive marketing and public relations, which some industry observers consider unprofessional.
4. Adoption and real-world application challenges: Like most cryptocurrencies, TRON faces the challenge of getting more businesses to accept its currency, TRX, and integrate their technology into their systems. While adoption appears promising on paper, implementation often presents difficulties.
Security
TRON incorporates several security measures to protect its network and its users. Its protocol is built around an architecture that includes advanced security features designed to safeguard against fraudulent transactions and malicious attacks. Here are a few of the key security measures:
1. Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) Mechanism: TRON uses Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism which is comparatively secure and efficient. In this system, TRX holders elect Super Representatives who validate transactions and create new blocks. This reduces the risk of centralization and enhances the networks security.
2. Decentralized Applications (DApps): The DApps on the TRON network have built-in security features to protect users from fraudulent activities. They are constructed in a way to prevent the most common attacks, such as replay attacks, and isolate potential security threats.
3. Cryptography: Like many blockchain platforms, TRON uses advanced cryptographic techniques to ensure secure transactions. This includes digital signatures to verify the identity of participants and encrypting data to protect it from unauthorized access.
4.Run-Time Protection: TRON's virtual machine provides run-time protection to validate code execution, restrain malicious activities and ensure contract safety.
Evaluations:
While TRON includes effective security measures, it's worth noting that no system is entirely impervious to risks. Past controversies related to alleged plagiarism have raised questions about the robustness of its original codebase, which could have implications for its security. Additionally, the security of DApps built on TRON depends extensively on the security measures implemented by individual DApp developers. Despite these potential risks, TRON's popularity and high transaction volume suggest that many users consider its platform sufficiently secure.
How Does TRON Work?
TRON operates by leveraging the features of blockchain and peer-to-peer (P2P) network technology. Its framework comprises three layers: the storage layer, the core layer, and the application layer.
The storage layer is responsible for block and state storage and is designed to be easy to modify hence making it more developer-friendly.
The core layer is where the bulk of the protocols set by TRON, such as consensus, account management, and smart contract operations are handled. It holds smart contracts creation and execution components, and handles the consensus through its Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) mechanism.
Meanwhile, the application layer is where developers on the TRON network create and customize their decentralized applications (DApps) and custom wallets.
Transactions on the TRON network operate using the protocol's native cryptocurrency, TRONIX (TRX), which are broadcasted to the entire network and validated by chosen Super Representatives via the DPoS mechanism. These Super Representatives validate the transactions by adding them to newly created blocks and recording them in the network. They are chosen by TRX coin holders in a continuous election process.
TRON's design focus on throughput, scalability, and availability enables the network to handle a high volume of transactions quickly and efficiently, making it attractive for developers looking to build and run advanced DApps. It aims to facilitate decentralized content sharing, allowing creators to directly engage with consumers, which reduces costs and enhances content availability.
What Makes TRON Unique?
TRON presents several unique features and innovations that distinguish it from other blockchain-based platforms:
1. High Performance: TRON uses a three-layer architecture (storage, core, and application layers) and leverages Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) consensus algorithm to ensure high-performance transactions. The structure and the process allow TRON to handle approximately 2,000 transactions per second.
2. Custom Smart Contracts: TRON supports a custom-built smart contract language, which simplifies the creation of complex agreements that automatically enforce and execute themselves. These are especially beneficial for developers of decentralized applications.
3. Decentralized Web: TRON's main innovation is its focus on the decentralized web. Its ultimate goal is to decentralize the internet, allowing users to access content without middlemen or centralized authority, which is significant for the creators of digital content.
4. Token Issuance: TRON makes it possible for users to freely issue their own tokens and create content, websites, and applications. This increases its functionality tremendously and makes it a more versatile ecosystem.
5. User Ecosystem and Incentive System: The TRON network's users play a different role in its governance and operations compared to many other blockchain platforms. Users vote for Super Representatives that produce blocks and validate transactions. These Representatives are then rewarded with TRX.
6. Java: The TRON protocol uses the Java programming language, which is widely recognized and used by developers worldwide. The use of Java lowers the entry barrier for many developers who want to interact with the TRON protocol.
How to sign up?
Signing up on TRON involves setting up a TRON Wallet, as the platform itself doesn't have a typical registration process. Here are the steps:
1. Choose a TRON Wallet: There are various TRON wallets available, both hardware and software, which include TronLink, TronWallet, Ledger, and others.
2. Download the Wallet: If you are opting for a software wallet, download it from the official site or trusted app stores to ensure security. For hardware wallets like Ledger, you will need to purchase the device.
3. Install & Open the Wallet: Install the downloaded wallet app and open it on your device.
4. Create a Wallet: Most wallets will have the 'Create Wallet' option on their home screen. Click on it.
5. Set a Password: You will be asked to set a strong password. Make sure to remember this password as you'll need it to access your wallet.
6. Backup Your Wallet: Usually, you'll be given a mnemonic phrase or recovery seed. This is very important to secure as it'll be needed to recover your wallet if you lose access.
7. Confirm Backup: After storing your mnemonic phrase securely, confirm that you've saved it.
After successfully following these steps, you can consider yourself registered in the TRON network through your TRON wallet. Please bear in mind that the exact process may slightly vary depending on the wallet you choose.
Can You Make Money?
In the TRON ecosystem, there are several ways that participants might potentially earn money. However, all come with their attendant risks, and careful consideration is necessary before investing time or money. Here are some possible ways:
1. Staking: TRON uses the Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) model. This means that by holding and staking TRONIX (TRX), TRON's native currency, participants can vote for Super Representatives, which could yield earnings from additional TRX tokens over time.
2. Trading TRX: As with other cryptocurrencies, participants can buy TRX at a low price and sell it when the price increases. However, this involves substantial risk, as cryptocurrency prices are notoriously volatile.
3. Building DApps: If you're a developer, you can make money by building and deploying decentralized applications on the TRON network. If your DApp becomes popular and is used widely, you might generate income.
4. Token Creation: TRON allows individuals and companies to issue their own token. If the token gets accepted by a large community, it can potentially make money.
5. Participating in ICOs: Some projects on the TRON network may hold Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs). Investing in an ICO requires a good understanding of the project and an assessment of its potential value. It's worth noting that this approach bears huge risks, as many ICOs have failed in the past.
As general advice, always do thorough research or seek advice from financial advisors before investing in any cryptocurrency. Avoid placing all your resources in one place and regularly keep yourself updated about TRON's latest news and developments, since this could potentially influence its price and your investment.
Conclusion
TRON represents a blend of potential high-yielding advantages, coupled with significant challenges and controversies to be navigated. On the positive side, its high throughput, scalability, and availability for DApps, along with its objective of supporting a decentralized Internet and facilitating cost-effective content sharing, make it an attractive option within the blockchain space. However, factors such as allegations of code plagiarism, a potentially less-than-fully decentralized model, and controversial marketing dynamics call for a cautious approach. A pragmatic evaluation of TRON would therefore suggest that while it does offer substantial potential, due diligence and continued monitoring of both achievements and challenges within its ecosystem are crucial for anyone considering a significant engagement with TRON, be it for participation, investment, or development purposes.
FAQs
Q: What is TRON's founding background and who are its key personnel?
A: TRON is a blockchain-based digital platform established in 2017 by the TRON Foundation, a non-profit organization located in Singapore, and it's led by CEO Justin Sun, a former representative of Ripple.
Q: What potential benefits and drawbacks does TRON have?
A: TRON's benefits include high throughput, high scalability, high availability for DApps, and the ability to support a decentralized Internet, while its drawbacks include accusations of code plagiarism, controversial marketing approaches by its founder, and challenges surrounding real-world application and adoption.
Q: What precautions has TRON taken to maintain network security?
A: TRON emphasizes security through its Delegated Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism, robust security measures within its DApps, advanced cryptography, and run-time protection in its virtual machine.
Q: How does the TRON network function?
A: TRON works on a three-layered architecture that includes the storage layer, core layer, and application layer, utilizing its native cryptocurrency, TRONIX (TRX) for transactions.
Q: What sets TRON apart from other blockchain platforms?
A: TRON stands out for its high-performance transaction structure, customized smart contract support, goals for a decentralized web, user-friendly token issuance, unique user ecosystem and incentive system, and employment of the Java programming language.
Q: How can one sign up for TRON?
A: Signing up for TRON involves selecting a TRON Wallet, downloading and installing the wallet on your device, creating a wallet within the application, and securely backing up your wallet.
Q: Can participants potentially earn money with TRON?
A: Yes, there are possibilities for earnings through staking TRX, trading TRX, developing DApps, creating tokens, and participating in ICOs within the TRON network.
Q: What's the general evaluation of TRON?
A: While TRON presents some appealing benefits like high throughput, scalability, and support for a decentralized Internet, it also brings along challenges related to allegations of plagiarism, controversial marketing strategies, and real-world application challenges, hence it suggests potential but with careful consideration and evaluation.
Risk Warning
Investing in blockchain projects carries inherent risks, stemming from the intricate and groundbreaking technology, regulatory ambiguities, and market unpredictability. Consequently, it is highly advisable to conduct comprehensive research, seek professional guidance, and engage in financial consultations before venturing into such investments. It's important to be aware that the value of cryptocurrency assets can experience significant fluctuations and may not be suitable for all investors.



Content you want to comment
Please enter...
Comment 8
News
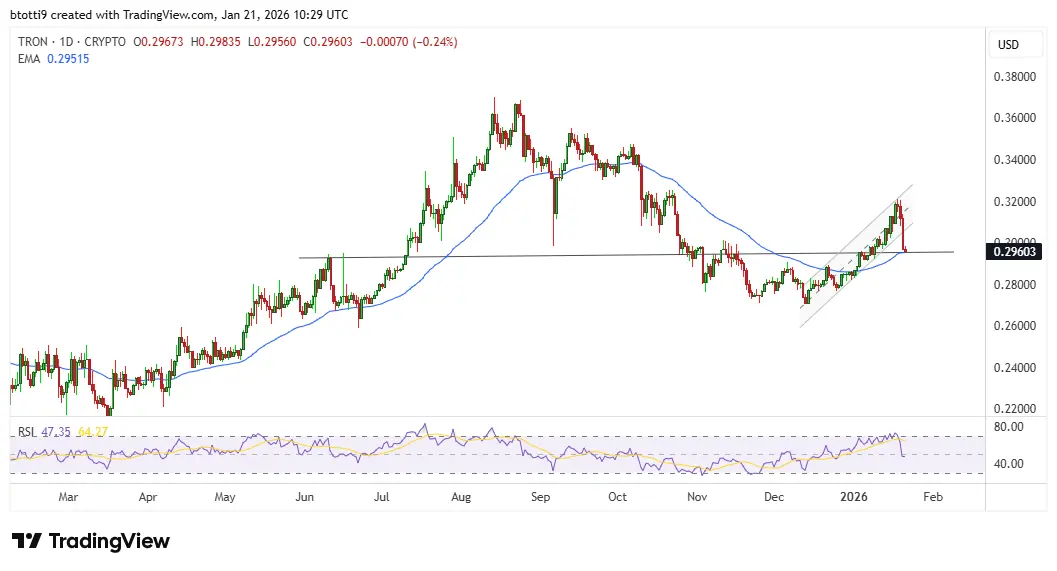
TRON extends downturn from $0.32 on broader crypto woes
TRON (TRX) has extended its decline amid a widespread cryptocurrency market pullback.Prices have dro
2026-01-22 02:03
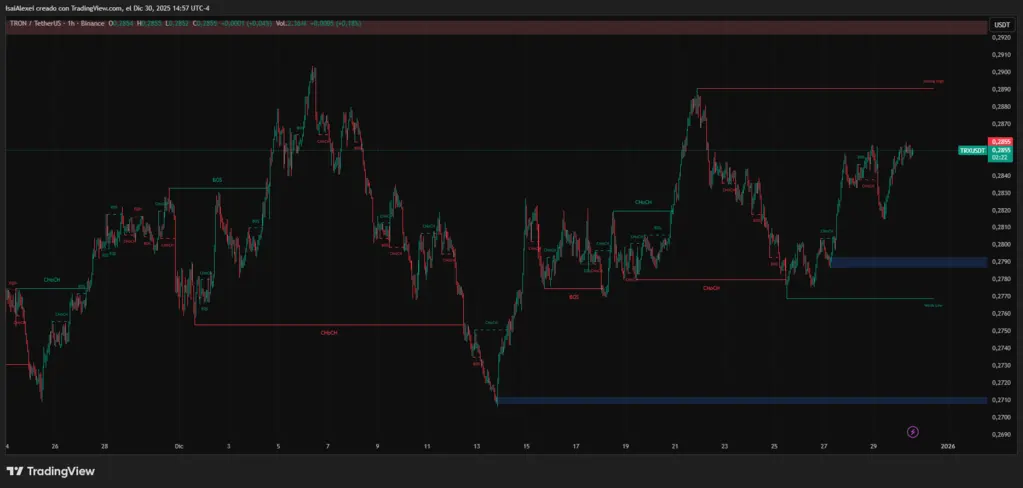
TRON (TRX) holds $0.28 after a fresh $18 million bet from Justin Sun
TL;DRTRX trades above $0.28, supported by an $18M capital injection from founder Justin Sun.Key tech
2025-12-31 06:02
TRON Network Hits Record User Growth as TRX Price Faces Worst Q4 Decline
User participation and trader engagement on the Tron network increased in December, with the total n
2025-12-26 13:02
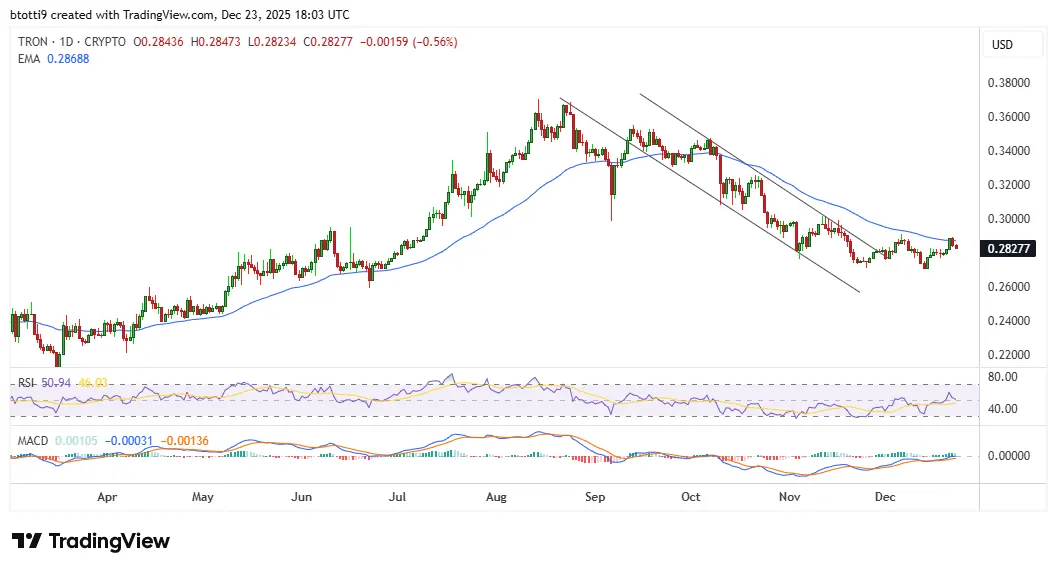
TRON price holds $0.28 as bulls show resilience
TRON price held above $0.28 despite heavy price declines across the crypto market.Bulls are showing
2025-12-24 04:00
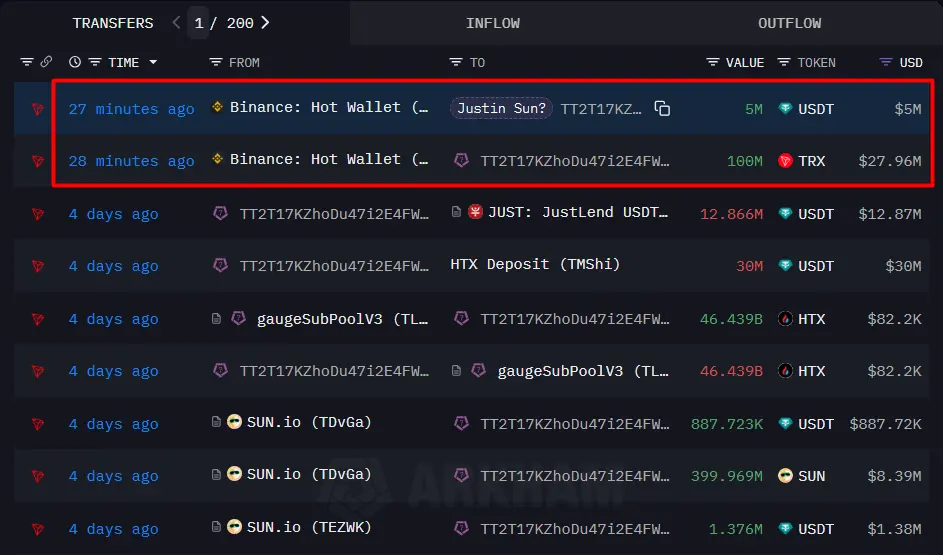
Tron Founder Justin Sun Withdraws 100,000,000 TRX From Binance
Recent on-chain data shows that a blockchain wallet associated with the Tron founder has withdrawn a
2025-12-04 02:04

THORWallet expands to Tron for advanced cross-chain swaps
Decentralized wallet ThorWallet has officially integrated the Tron blockchain, enabling users to con
2025-11-29 05:02

Scarletc
2023-12-06 20:17
TRON is a blockchain designed to run smart contracts and other DeFi applications. TRX is the platform’s native cryptocurrency, which powers its proof-of-stake consensus algorithm.
Neutral