DeFi
Overview of DeFi
Decentralized finance, frequently referred to as DeFi, represents a shift in the financial system toward a fully open, permissionless, and highly interoperable protocol stack built on public smart contract platforms. It is a broad categorization of financial applications that are being developed on top of blockchain systems. DeFi draws inspiration from blockchain, the technology behind the digital currency bitcoin, which allows several entities to hold a copy of a history of transactions, meaning it isn't controlled by a single, central source.
The term DeFi, short for"decentralized finance", was coined by developers and technologists who are working to recreate traditional financial systems with blockchain technology. It was popularized around 2018-2019, largely stemming from Ethereum developers and others in the open source blockchain community. However, it lacks defined founders or a formalized central entity.
DeFi is characterized by a number of common features including its accessibility to anyone with an internet connection, its operation 24/7, provable transparency, interoperability with other products and services, and programmatic executions (smart contracts).
The use of these different open-source protocols to perform financial functions in a decentralized manner has opened up an array of possibilities for financial services like borrowing, lending, asset swapping, yield farming, and more without the need for traditional intermediaries such as banks. Despite its advantages, it‘s also worth highlighting that it’s still a developing field with its own risks and challenges.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Open accessibility to anyone with an internet connection | Risks of smart contract vulnerabilities |
| Operational 24/7 without any downtime | Complex user interface for non-technical users |
| Transparency through publicly verifiable transactions | Potential for high price volatility |
| Interoperability with other blockchain-based products and services | Lack of legal clarity and regulatory framework |
| Programmatic executions through smart contracts | Risks of anonymity and lack of accountability |
| Elimination of traditional intermediaries like banks | High gas fees on Ethereum network |
Sure, here are the pros and cons of DeFi in detail:
Pros:
1. Open accessibility to anyone with an internet connection: DeFi system does not require any physical infrastructure or geographic location. It is accessible to anyone, anywhere with an internet connection. This could potentially provide financial services to a large unbanked population around the world.
2. Operational 24/7 without any downtime: DeFi systems are built to be operational all the time. Since they are decentralized and not controlled by any single entity, they do not face the risk of downtime, unlike traditional financial systems.
3. Transparency through publicly verifiable transactions: Since they are built on blockchain, DeFi systems maintain a clear and transparent record of all transactions. This transparency can go a long way in ensuring the trust and security of operations.
4. Interoperability with other blockchain-based products and services: DeFi solutions are designed to integrate and work together. This allows users to seamlessly interact with multiple services without the need to exit the system.
5. Programmatic executions through smart contracts: The use of smart contracts allows DeFi services to automatically execute transactions based on predefined rules. This eliminates the need for manual processing and reduces the likelihood of errors.
6. Elimination of traditional intermediaries like banks: Since DeFi operates on a peer-to-peer network, it does away with traditional intermediaries such as banks. This often results in faster transactions and, in many cases, lower costs.
Cons:
1. Risks of smart contract vulnerabilities: While smart contracts automate processes in the DeFi ecosystem, they also introduce new vulnerabilities. If these contracts contain bugs or are not properly audited, they can be manipulated by malicious actors, resulting in losses.
2. Complex user interface for non-technical users: The technology and concept behind DeFi can be complex and intimidating to non-technical users, which could limit adoption.
3. Potential for high price volatility: DeFi is a nascent field and therefore subject to high price volatility. This can lead to substantial gains, but also, substantial losses.
4. Lack of legal clarity and regulatory framework: The lack of a clear regulatory framework can create uncertainty and pose risks to DeFi participants. Regulation could provide a safer environment, but it is often unable to keep pace with fast-evolving technology.
5. Risks of anonymity and lack of accountability: While the anonymity provided by DeFi applications upholds the privacy of its users, this also opens them up to malicious activities and fraud due to lack of accountability.
6. High gas fees on the Ethereum network: The high gas fees on the Ethereum network, where a majority of the DeFi projects operate, is a significant drawback. High transaction costs can detract from the accessibility and affordability aspects of DeFi.
Security
DeFi projects build their security measures around a number of fundamental principles inherent to blockchain technology. Here are several of these measures, along with their evaluations:
1. Smart Contract Audits: Before deployment, DeFi smart contracts often undergo thorough audit process by independent third-party security firms to ensure the codes do not harbour exploitable bugs. However, audits cannot guarantee 100% security as the complexity of smart contracts may lead to oversights.
2. Decentralization: By virtue of being decentralized, DeFi applications are robust against single points of failure, such as server outages, making them resilient. However, this does not protect against instances where a major fraction of network participants collude to alter transactions, otherwise known as a 51% attack.
3. Encryption: Confidential data within the DeFi ecosystem is secured through cryptographic algorithms. While this is an effective security measure, it is not entirely impenetrable. With advancing technology, the threat of quantum computing that could potentially break current encryption standards looms.
4. Transparency: All transactions on a blockchain are visible to all network participants which deters fraudulent activities. But the anonymity linked with such transactions could make it challenging to track and reclaim stolen funds.
5. Multi-Signature wallets: These wallets require multiple private keys to authorize a blockchain transaction, adding an extra layer of security. However, if these private keys are not stored securely, they could still be susceptible to theft.
6. Use of Governance Tokens: Some DeFi projects use governance tokens that allow holders to vote on changes to the protocol, including security enhancements. However, if majority of these tokens fall into the hands of malicious actors, they could potentially make changes that undermine the protocols security.
In conclusion, while DeFi boasts a number of innovative security measures, it is important to note that no system could be entirely foolproof. The current security infrastructure in DeFi is still maturing and as DeFi continues to evolve, new security challenges will undoubtedly emerge. Thus, anyone engaging with DeFi should exercise caution and proper risk management practices.
How Does DeFi Work?
DeFi operates through the use of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies, primarily Ethereum, to recreate and improve financial systems and services. It aims to provide a global, open alternative to every financial service we use today — from savings, loans, trading, insurance, and more, accessible to anyone in the world with a smartphone and internet.
The functioning of DeFi is based on three core mechanisms: smart contracts, decentralization, and blockchain technology.
1. Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts formulated as a collection of code and data, stored in a specific address of the blockchain. This code governs what conditions must be met for transfers of cryptocurrency to be validated.
2. Decentralization: Traditional financial systems are centralized - they rely on intermediaries like banks and governments to function. DeFi, on the other hand, is fundamentally decentralized. It removes the need for intermediaries by using an inclusive peer-to-peer network that interacts with the help of blockchain.
3. Blockchain: A blockchain is a type of distributed ledger, where each node in the network holds its own copy of the ledger. All transactions are added to this ledger, further enhancing transparency.
In practice, when someone interacts with a DeFi application - known as a dApp - theyre interacting with a backend of smart contracts on a blockchain. With smart contracts, you can create rules that self-execute. When rules and conditions are pre-programmed into the contract, blockchain transactions can become automatic.
Moreover, DeFi relies on tokenization, which is the process of representing real-world assets in digital form on a blockchain. This fundamental element enables the creation of various decentralized applications with different functionalities, from lending and borrowing to derivatives and exchanges. By tokenizing assets, a person's ownership rights can be proven and securely stored, and financial transactions do not need to be entrusted to third parties. In this way, DeFi is leading the way towards a globally accessible and inclusive financial system.
What Makes DeFi Unique?
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, brings several unique features or innovations to the table, which are reshaping the financial system. Here are some of them:
1. Permissionless and Open Source: DeFi applications are often open source and permissionless, meaning anyone can view the underlying code and contribute. Furthermore, anyone with an internet connection can access these services without needing to fulfill certain criteria or submit formal applications.
2. Interoperability: DeFi apps are built on public blockchains such as Ethereum which allow seamless integration and interaction between different apps due to their shared infrastructure. This “money lego” effect can lead to innovative products and services.
3. Programmability: DeFi extensively capitalizes on the programmable aspect of smart contracts on the blockchain. This allows for the creation of complex automated financial instruments that can be run and audited by machines.
4. Non-custodial: Many DeFi applications provide non-custodial services meaning users maintain full control over their assets, which is not the case with traditional banking and financial services where funds are entrusted to the institution.
5. Financial Inclusion: Due to its global accessibility, DeFi potentially opens up financial services to populations worldwide that are unbanked or underserved by traditional financial institutions.
6. Transparency: Transactions made on blockchain are publicly verifiable, hence providing unprecedented transparency in comparison to the traditional financial system.
7. Yield Farming: Unique to DeFi, yield farming allows users to earn rewards for participating in a DeFi protocol. This has led to innovative financial strategies and created new forms of user behavior.
These unique features represent foundational shifts in the way financial services could be structured and delivered, paving the way for more transparent, accessible, and equitable financial structures.
How to sign up?
Signing up for most DeFi platforms is relatively straightforward and does not require a formal sign-up or account creation process like traditional financial institutions demand. Here's a general process on how users typically interact with DeFi services:
1. Crypto Wallet: First, you would need a cryptocurrency wallet that supports Ethereum, since most DeFi applications are built on the Ethereum network. Metamask is one example, but there are many other wallets available. Ensure your wallet is secure and always keep your keys private.
2. Buy Ethereum: Next, you have to buy Ethereum (ETH) or any other supported ERC-20 token, which you'll use in transactions on the DeFi platform. You can purchase ETH from various centralized exchanges like Coinbase or Binance. After buying, transfer your ETH to your wallet.
3. Connect to a Platform: Now you can go to a DeFi platform of your choice. Most DeFi platforms will have an option to"Connect Wallet" on their interface. You need to authorize your wallet to connect with the platform.
4. Interaction: Once your wallet is connected, you can now interact with the platform. This could be for lending, borrowing, yield farming, staking, swapping tokens, or any other function that the DeFi platform provides.
Remember that DeFi can be risky and its important to carry out due diligence on the platforms you intend to use. It's also vital to understand transaction fees (Gas fees in Ethereum) as they can have a major impact on your activities.
Can You Make Money?
Yes, there are several ways users can potentially earn money by participating in DeFi platforms, often yielding higher returns than traditional financial products. Here are some ways and advice on making money with DeFi:
1. Lending: Users can earn interest by lending their cryptocurrencies to others through platforms such as Aave and Compound. Before lending, users should evaluate the platform's security measures and the interest rate being offered, considering the potential risk of borrower default.
2. Yield Farming: This is a process where users provide liquidity to DeFi protocols and are rewarded with tokens. It often provides high returns but also comes with higher risks, largely due to the complex strategies involved and the instability of reward tokens' prices.
3. Staking: Some DeFi platforms offer staking, where users commit their tokens to a network to maintain its operations (like transaction validation), and they're rewarded with interest. However, staked tokens are often locked for certain periods and may face penalties for early withdrawal.
4. Trading: Sophisticated users may profit from trading digital assets on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap. However, trading involves significant risks due to the price volatility of cryptocurrencies.
5. Liquidity Mining: This involves providing liquidity to a decentralized exchange and earning rewards. However, it comes with risks such as"impermanent loss," and the costs may outweigh the rewards, especially in volatile markets.
Advice:
- Research: Understand the platform, its developers, the smart contract it's built on, and its overall performance before investing.
- Risk Management: As the potential for profits increases, so does risk. Diversify your portfolio and only invest what youre willing to lose.
- Be Aware of Gas Fees: This is a fee charged for transactions on the Ethereum network. The fees fluctuate depending upon the demand for the network, and high gas fees can eat into your profits.
- Don't Chase After High Returns Blindly: Extremely high promises of returns are generally accompanied by equally high risks. Be cautious when dealing with such platforms.
- Stay Updated: The DeFi world moves at a rapid pace, both developing and creating risks quickly. It's essential to stay updated with the changes.
Remember, participating in DeFi projects entails risk, so due diligence is crucial. DeFi platforms should be used as financial tools, not as a way to get rich quick.
Conclusion
Decentralized finance, or DeFi, offers tremendous possibilities, from providing financial services to unbanked populations worldwide, promoting transparency and financial inclusivity, to the potential for high returns on investments. Its unique features of interoperability, programmability, non-custodial services, while eliminating the need for traditional intermediaries have positioned DeFi as a strong contender for future financial systems. However, it is also accompanied by significant risks. The threat of smart contract vulnerabilities, high price volatility, complex user interfaces, and regulatory uncertainties present critical challenges. Therefore, it is crucial for participants to conduct thorough research and exercise caution while navigating the DeFi space. DeFi is a fast-evolving field, and its long-term sustainability will depend on how successfully it addresses these challenges.
FAQs
Q: What does DeFi refer to?
A: DeFi, or Decentralized Finance, represents a broad array of financial applications being created on top of blockchain platforms.
Q: How does DeFi propose to revolutionize finance?
A: DeFi aims to remodel finance by enabling traditional financial services, like lending and insurance, with a decentralized, open-source, and permissionless approach using blockchain technology.
Q: What is a"smart contract" in the context of DeFi?
A: In DeFi, a smart contract is a self-executing code stored on a blockchain designed to carry out predefined set rules and validate transfers of cryptocurrency.
Q: Is there risk involved in participating in DeFi?
A: Yes, DeFi involves significant risks, such as smart contract vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainties, market volatility, high gas fees, and other technical risks.
Q: How can one get started with DeFi?
A: Getting started with DeFi typically requires an Ethereum-compatible wallet, some amount of ETH or other supported tokens, and a connection to a DeFi platform where you can perform financial operations.
Q: How can a participant earn money from DeFi?
A: Participants can earn money from DeFi via lending, yield farming, staking, trading on decentralized exchanges, and liquidity mining, while being cognizant of the associated risks.
Q: What is yield farming in the context of DeFi?
A: Yield farming is a DeFi practice where individuals provide liquidity to a DeFi protocol in order to earn reward tokens, usually generating potentially high returns.
Q: Can anyone in the world use DeFi?
A: Yes, anyone with an internet-connected device can access and participate in DeFi's open, inclusive, and global financial services.
Q: Are DeFi transactions transparent?
A: Yes, transactions in DeFi are recorded on the blockchain, providing full transparency, although the identity of the participants is generally kept anonymous.
Q: Is DeFi regulated?
A: Currently, DeFi exists in a legal grey area with lack of clear regulation or legal framework, adding to its risk factor.
Risk Warning
Investing in blockchain projects carries inherent risks, stemming from the intricate and groundbreaking technology, regulatory ambiguities, and market unpredictability. Consequently, it is highly advisable to conduct comprehensive research, seek professional guidance, and engage in financial consultations before venturing into such investments. It's important to be aware that the value of cryptocurrency assets can experience significant fluctuations and may not be suitable for all investors.
Website

sjhtop.com
Server Location
United States
Most visited countries/areas
--
Domain
sjhtop.com
ICP registration
--
Website
--
Company
--
Domain Effective Date
--
Server IP
172.67.174.71



Content you want to comment
Please enter...
News
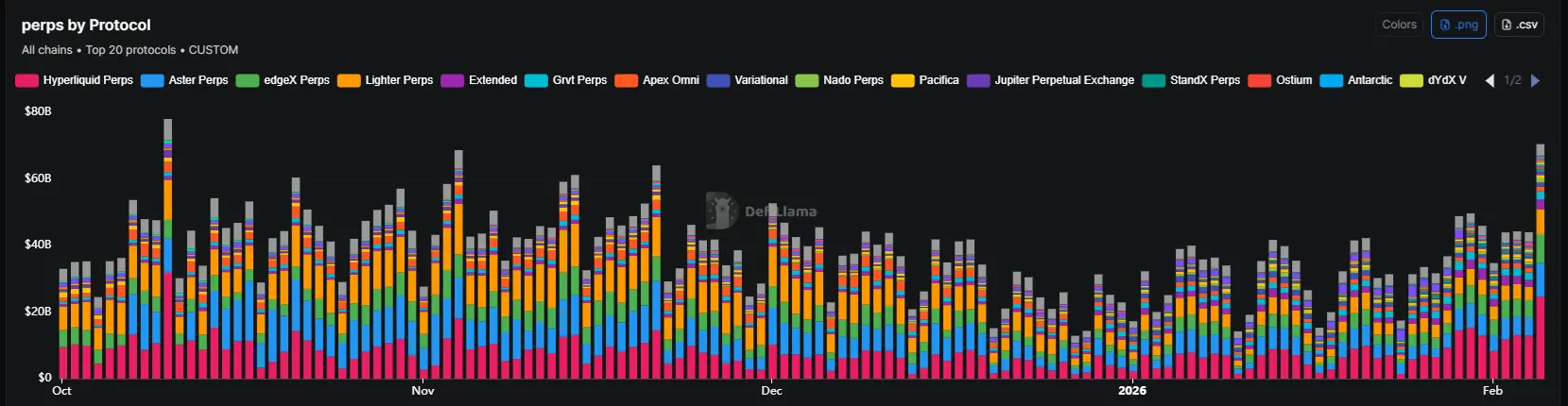
DeFi protocols avoid shut downs despite near-record activity in latest market capitulation
DeFi activity moved to the highest levels since the October 10-11 crash. The recent market capitulat
2026-02-07 02:03

XRP Community Gains DeFi Lending Through Flares FXRP Rollout
TL;DRFlare activated FXRP lending via Morpho, letting $XRP holders earn interest or borrow stablecoi
2026-02-04 08:02
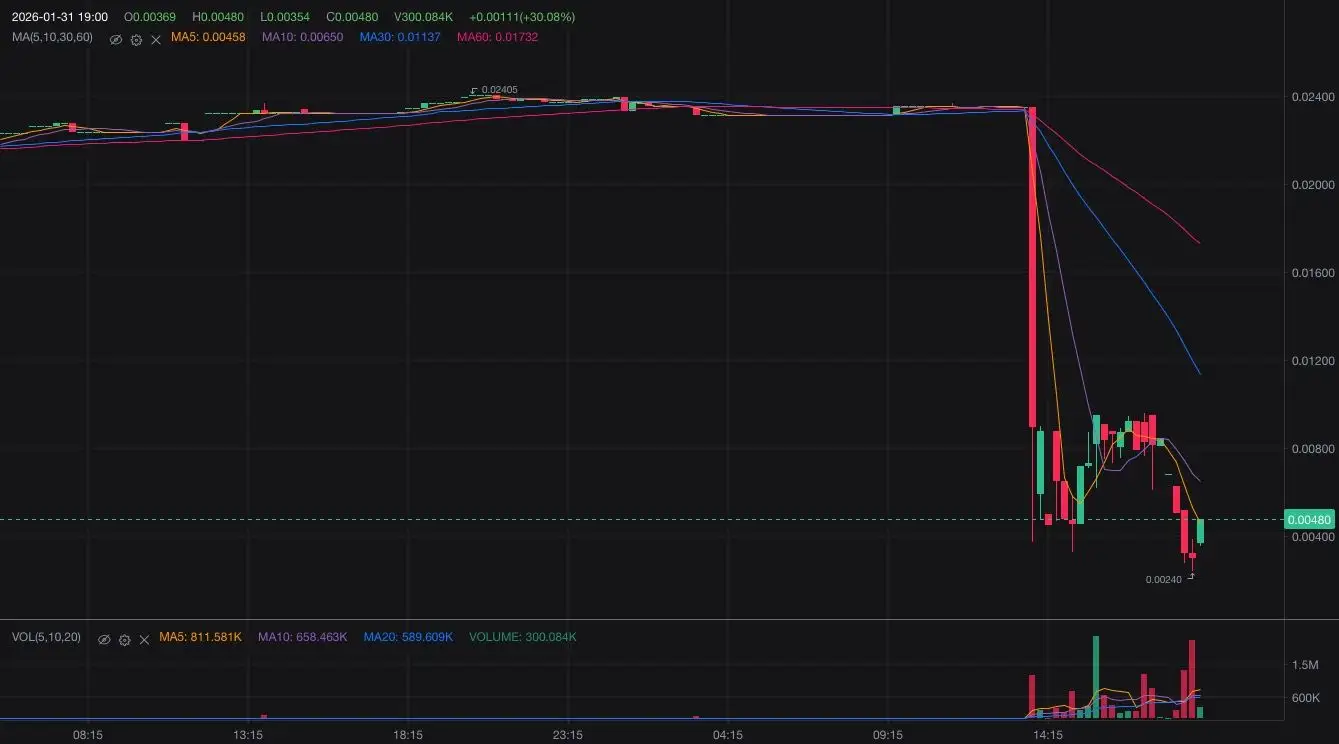
Solana DeFi platform step finance hit by $27 million treasury hack as token price craters
Step Finance, a decentralized finance (DeFi) portfolio tracker built on Solana, said some of its tre
2026-02-01 03:02
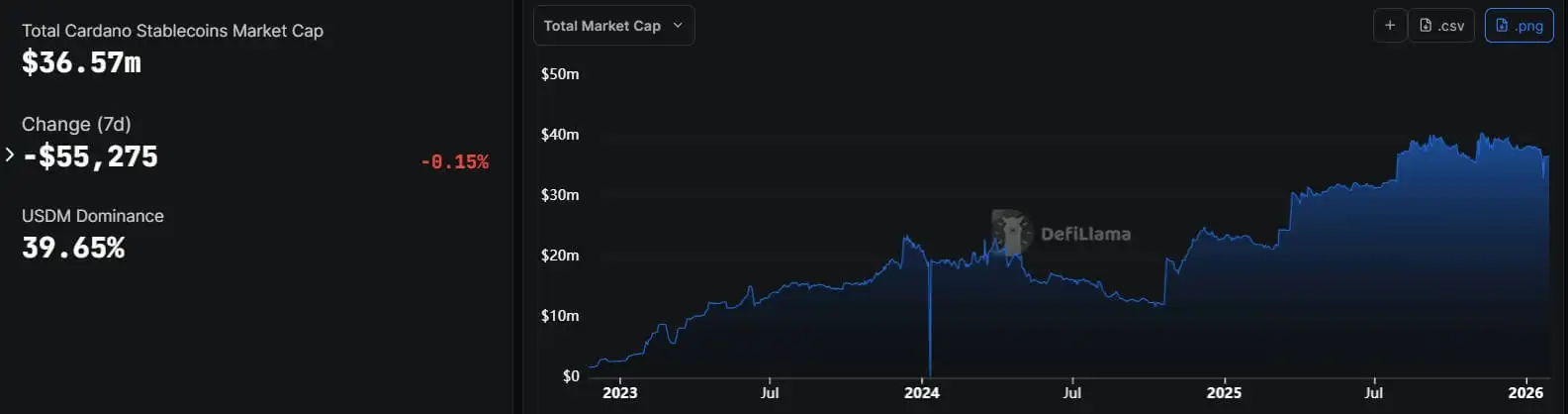
Cardano bets on USDCx to close liquidity gap and boost DeFi
On Jan. 30, Cardano founder Charles Hoskinson announced that he has signed an integration agreement
2026-01-31 06:02
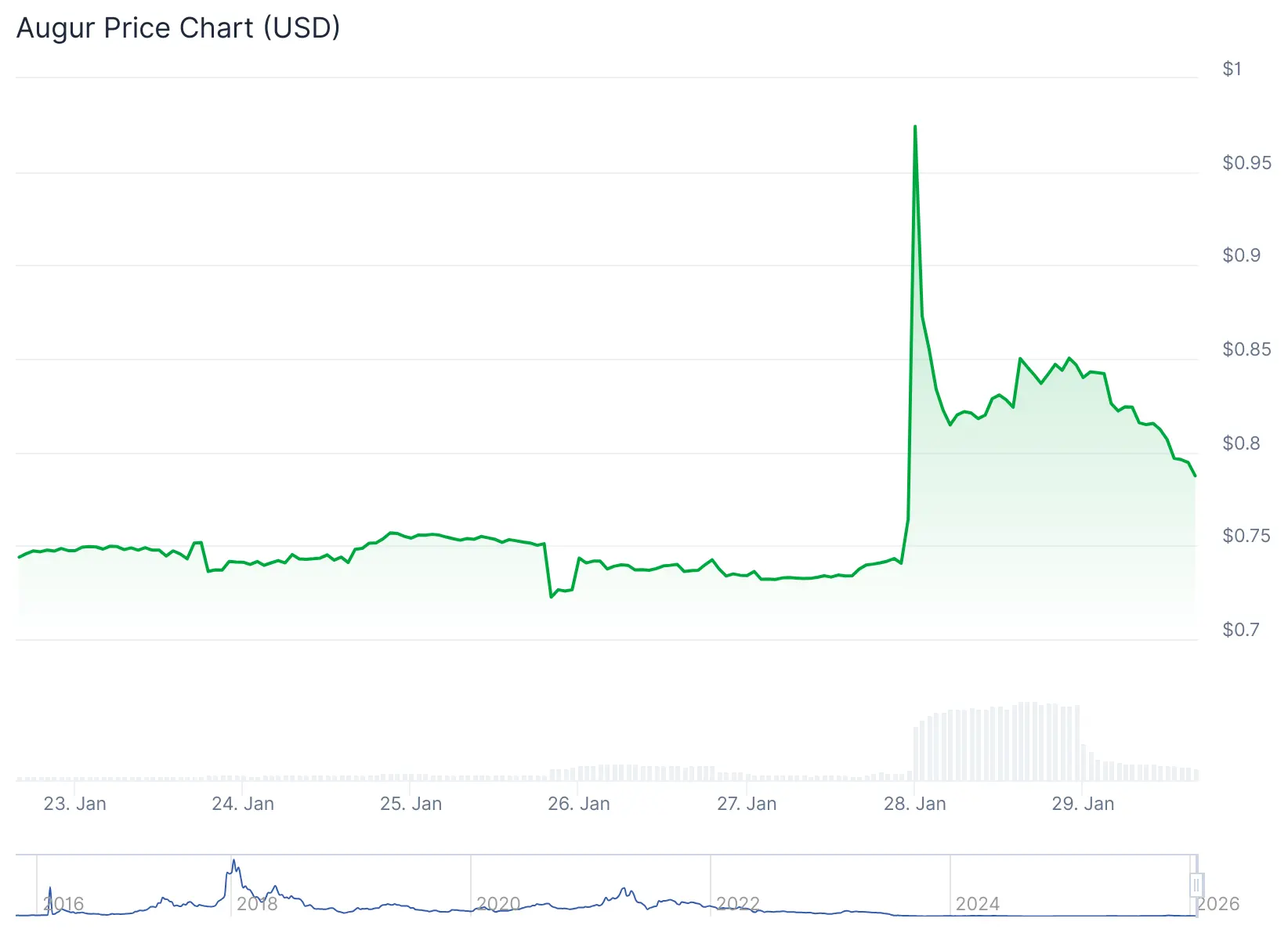
Augur Reveals Lituus Oracle Infra to Fight Market Manipulation Across DeFi
Early decentralized prediction market protocol Augur has released new oracle infrastructure designed
2026-01-30 00:02
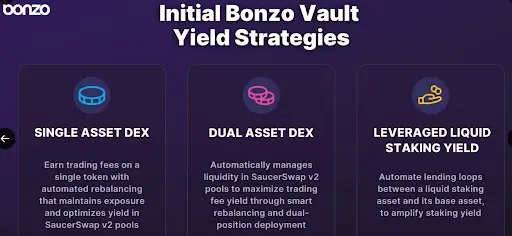
Hedera DeFi Gets Automated Yield as Bonzo Vaults Enter Beta
Bonzo Vaults offers automated yield strategies via EVM smart contracts that rebalance and auto-compo
2026-01-29 21:03