BTC TO PM
Overview of Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency, created in 2009 by an unknown person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. The main novelty of Bitcoin resides in its technology called blockchain, which operates without a central authority or government. Bitcoin transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded on a public ledger known as a blockchain. Bitcoin can be exchanged for other currencies, products, and services. Bitcoin is often referred to as the first cryptocurrency, although prior systems existed, and it is more correctly described as the first decentralized digital currency. The identity of Satoshi Nakamoto is still a mystery.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
| User Autonomy | Potential for loss |
| Peer-to-Peer Focus | Subject to high price volatility |
| Low Transaction Fees for International Payments | Not accepted by every merchant |
| Accessibility | Can be used for illegal transactions |
Pros of Bitcoin:
1. User Autonomy: One of the primary draws of Bitcoin for many users is autonomy. Digital currencies, such as Bitcoin, allow users more discretion over their own money than traditional banking systems. In theory, they can control how they spend their money without dealing with an intermediary authority like a bank or government.
2. Peer-to-Peer Focus: Bitcoin is designed to allow its users to send and receive payments with an acceptable level of privacy as well as any other form of value. Bitcoin's system operates in a peer-to-peer manner, and transactions occur directly between users without needing a mediator.
3. Low Transaction Fees for International Payments: Bitcoin is not controlled by any government or organization, which makes international transactions being done at relatively low costs compared to traditional banking systems and online money transfers.
4. Accessibility: Because users can send and receive bitcoins with only a smartphone or computer, it is potentially available to populations of users without access to traditional banking systems, credit cards, and other methods of payment.
Cons of Bitcoin:
1. Potential for Loss: Bitcoin wallets can be lost. If a hard drive crashes, or a virus corrupts data, and the wallet file is not backed up, bitcoins are gone forever. Additionally, if a user loses their private keys, all Bitcoins they possess are lost.
2. Subject to High Price Volatility: Bitcoin's price is extremely unstable, it can increase or decrease unpredictably due to its young economy, novel nature, and sometimes illiquid markets. This can result in large price differences between exchanges.
3. Not Accepted by Every Merchant: Many companies do not accept Bitcoin as a form of payment, limiting the currency's usefulness.
4. Can be Used for Illegal Transactions: Because of the anonymity Bitcoin transactions offer, it can be used for illegal activities. This could include transactions conducted in the black market or other illegal activities.
Security
Bitcoin implements several security measures to protect its network and users. First and foremost, it uses cryptographic technology. Each Bitcoin transaction involves a private key, which is a secret number that allows bitcoins to be spent. Every Bitcoin address has a matching private key, which is saved in the Bitcoin wallet of the person who owns the balance. The private key proves that the transaction came from the owning wallet. This cryptography ensures the security of transaction processing and protects from double spending.
In addition, the use of blockchain technology, where all transaction data is stored publicly in blocks and distributed across thousands of computers worldwide, significantly improves security. This makes it nearly impossible for anyone to alter transaction data once it is in the blockchain as it would require the alteration of all subsequent blocks and coordination of the network majority.
Also, it's crucial to highlight that Bitcoin transactions are pseudonymous. Each user operates with a unique address that isn‘t linked to their personal information. However, because transactions and addresses are stored in the blockchain publicly, Bitcoin doesn’t provide complete anonymity but provides a certain level of confidentiality.
Despite these security measures, Bitcoin also has its vulnerabilities. Its important to note that most Bitcoin thefts and losses occur at the intersections where Bitcoin meets traditional, centralized financial systems, such as exchanges and wallets. These platforms can be hacked, and people can lose their private keys in phishing scams.
In conclusion, while Bitcoin's inherent technology provides a secure framework, the security of one's bitcoin largely comes down to personal practice, including the use of two-factor authentication, good internet security hygiene, and the use of secure, preferably offline, wallets for storing your Bitcoin.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
Bitcoin operates on a technology known as blockchain, a decentralized and public digital ledger that records every bitcoin transaction across many computers to ensure any involved record cannot be altered retroactively, without the alteration of all subsequent blocks. Here's a simplified sequence of how it works:
1. New Transactions: When a Bitcoin user sends a BTC transaction, the user's software, also known as a “Bitcoin Wallet,” creates a transaction message, necessary for the transaction to go through. This would include the recipient's public key (their bitcoin address).
2. Transaction Verification: The transaction is broadcasted to the network where network nodes or miners validate the transaction. Validation includes checking the transaction details using a process known as 'cryptographic hash functions.' In simple terms, they are making sure the transaction is legitimate.
3. Mining: Once verified, the transaction is bundled with other transactions, forming a new data block for the blockchain. Miners then compete to validate the new entries (transactions) in the block by solving a complex mathematical problem. The first miner to solve it “wins” the block and is rewarded with new bitcoins, and the block is added to the blockchain.
4. Blockchain Addition: Post verification, the transaction block is added to the existing blockchain, in a way that is unalterable and permanent. The money moves to the receiver's account once the block is added to the blockchain.
5. Transaction Completion: Once the process is completed, the recipient's wallet, online or offline depending on where it is stored, would show the received bitcoins.
It's important to note that the whole process is decentralized. Unlike traditional transaction systems, there isn't a single authority that verifies your transaction. This highlights one of Bitcoin's core beliefs: being a decentralized and open-to-all system.
What Makes Bitcoin Unique?
Bitcoin has several unique features and innovations:
1. Decentralization: One of the most distinguishing features of Bitcoin is that it is decentralized. There is no central authority or government regulating or controlling Bitcoin. This decentralization is achieved through blockchain technology.
2. Blockchain Technology: Bitcoin uses blockchain technology to maintain a public ledger of all transactions on the network. The blockchain is maintained by multiple random nodes, which makes it nearly impossible to alter any transaction data.
3. Cryptography: Bitcoin uses cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and control the creation of additional Bitcoin units. It uses the SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 2) cryptographic algorithm designed by the United States National Security Agency.
4. Peer-to-Peer Transactions: Bitcoin facilitates direct transactions between two parties without requiring a trusted third party or intermediary, such as a bank or financial institution.
5. Finite Supply: There are only 21 million bitcoins that can be mined, providing a predictable and limited supply.
6. Mining: The process of adding new transactions to the blockchain is referred to as “mining”. Miners compete with each other to solve complex mathematical problems to add a new block to the blockchain. This process ensures the trust and security of the transaction.
7. Anonymity & Privacy: Although all transactions are recorded publicly on the blockchain, these transactions are linked to a cryptographic address and not necessarily to an individual identity, which offers a level of privacy and anonymity.
8. Divisibility: Each Bitcoin can be divided down to eight decimal places. The smallest unit, 0.00000001 Bitcoin, is known as Satoshi.
9. Digital Form: Being a digital currency, Bitcoin doesn't have a physical form. This feature allows quick and convenient transactions over the internet.
How to sign up?
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency, so you don't “sign up” for Bitcoin in the way you might with a website or a service. Instead, you create a Bitcoin wallet. The process for setting up a Bitcoin wallet can vary slightly depending on which wallet provider you choose, but in general, you can expect to follow a process similar to:
1. Choose a Bitcoin Wallet: You'll first need to choose a Bitcoin wallet that suits your needs. Wallets can be online or offline, mobile or desktop, hardware or software. Do your research, not just into security and legitimacy, but also into practicality. Does wallet software look like you can understand how to use it? Is it recommended by trusted sources?
2. Download/Install the Wallet: If the wallet is software or a mobile app, it will need to be downloaded and installed on your device. Make sure to download software from the official wallet provider's website to avoid any phishing scams.
3. Create Your Account: Once it is downloaded, you can create your account. You may need to provide a username, a strong password, and email to recover your password.
4. Set Up Security Measures: Most wallets will encourage or even demand that you employ extra security measures, like two-factor authentication.
5. Backup Your Wallet: Usually, you'll be encouraged to create a backup of your new wallet. This could come in the form of a randomly generated phrase that you must write down (not save on a computer where it may be vulnerable to hacking).
6. Get a bitcoin address: Once everything is set up, the wallet will provide you with a Bitcoin address—a, a unique identifier that people can use to send you Bitcoin.
7. Buy Bitcoin: Now, you can use your wallet to buy Bitcoin from a cryptocurrency exchange using traditional money, or you can receive Bitcoin from other users.
Remember, if you lose access to your Bitcoin wallet, you've lost your bitcoins. Also, if anyone else gains access to your wallet, they can take your bitcoins. Thus, security measures are crucial.
Can You Make Money?
Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies present opportunities for potential financial gain, mostly through trading or investing, and sometimes through engaging in the process known as mining. Please note, this is different than a typical 'program' where you would earn incentives or rewards.
1. Trading & Investing: Many people have profited from buying Bitcoin at a low price and then selling it at a higher one. There are various trading strategies such as day trading, swing trading, and holding for the long term, depending on each individual's risk tolerance and market knowledge.
2. Mining: The process of creating new Bitcoins by solving complex mathematical problems is known as mining. However, doing this requires considerable computing power and technical expertise.
3. Earning Bitcoin: Some platforms and websites offer Bitcoin as payment for performing certain tasks or services.
Despite these opportunities, it's important to stress that dealing with Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies also involves substantial risk. Market prices are notoriously volatile and investing in cryptocurrencies is not recommended for those who can't afford to lose the amount they invest. Before getting engaged with Bitcoin or any other cryptocurrency, thorough research and possibly consultation with a financial advisor is recommended. At all times, security must be a top priority to protect one's holdings from hacking or fraud.
Conclusion
Bitcoin, since its inception in 2009, has become the pioneer of cryptocurrencies and a prominent player in the field of digital payments. Its innovative utilization of blockchain technology and cryptography is a revolutionary innovation in modern financial transactions. While these characteristics introduce significant advantages, such as user autonomy, peer-to-peer focus, lower transaction fees for international payments, and accessibility, it's important to be mindful of the associated risks. High price volatility, potential for loss, limited acceptance by merchants, and its potential use for illegal activities continue to present challenges. Ultimately, the value and potential of Bitcoin may depend significantly on how these issues are addressed in the future. Despite these obstacles, Bitcoin undeniably paved the way for the acceptance and mainstreaming of decentralized digital currencies.
FAQs
Q: What is Bitcoin and who created it?
A: Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer digital currency established in 2009 by an individual or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto.
Q: Can I make profits with Bitcoin?
A: Yes, through trading, investing, or mining, however, each method poses significant risks given the volatile nature of digital currencies.
Q: How can I secure a Bitcoin wallet?
A: Bitcoin wallet security can be enhanced by implementing strong passwords, two-factor authentication, regularly updating your wallet software, and keeping backups of your wallet.
Q: What are the main advantages and disadvantages of Bitcoin?
A: Bitcoin's primary advantages are user autonomy, peer-to-peer transactions, comparatively low international transaction fees, and accessibility, while its main disadvantages are price volatility, potential for irreversible losses, limited acceptance by vendors, and potential utilization for illicit activities.
Q: Can Bitcoin guarantee anonymity?
A: Bitcoin offers a degree of privacy through pseudonymous transactions, but due to its public ledger, it doesn't provide complete anonymity.
Q: What determines the value of a Bitcoin?
A: The value of Bitcoin is largely determined by the balance of supply and demand in the market, and it can be influenced by factors such as the number of active users, overall market sentiment, regulatory news, and macroeconomic trends.
Q: What is Bitcoin mining?
A: Bitcoin mining is the process of validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain, which involves solving complex computational puzzles; miners who solve these puzzles are awarded with new Bitcoins.
Q: Can I lose my Bitcoins?
A: Yes, if you lose access to your Bitcoin wallet, for instance, by losing the private key or through hacking, your Bitcoins could be irretrievably lost.
Risk Warning
Investing in blockchain projects carries inherent risks, stemming from the intricate and groundbreaking technology, regulatory ambiguities, and market unpredictability. Consequently, it is highly advisable to conduct comprehensive research, seek professional guidance, and engage in financial consultations before venturing into such investments. It's important to be aware that the value of cryptocurrency assets can experience significant fluctuations and may not be suitable for all investors.
Website

bitcointoperfectmoney.com
Server Location
France
Most visited countries/areas
--
Domain
bitcointoperfectmoney.com
ICP registration
--
Website
--
Company
--
Domain Effective Date
--
Server IP
92.113.24.91

btctopm.com
Server Location
France
Most visited countries/areas
--
Domain
btctopm.com
ICP registration
--
Website
--
Company
--
Domain Effective Date
--
Server IP
92.113.24.91



Content you want to comment
Please enter...
News
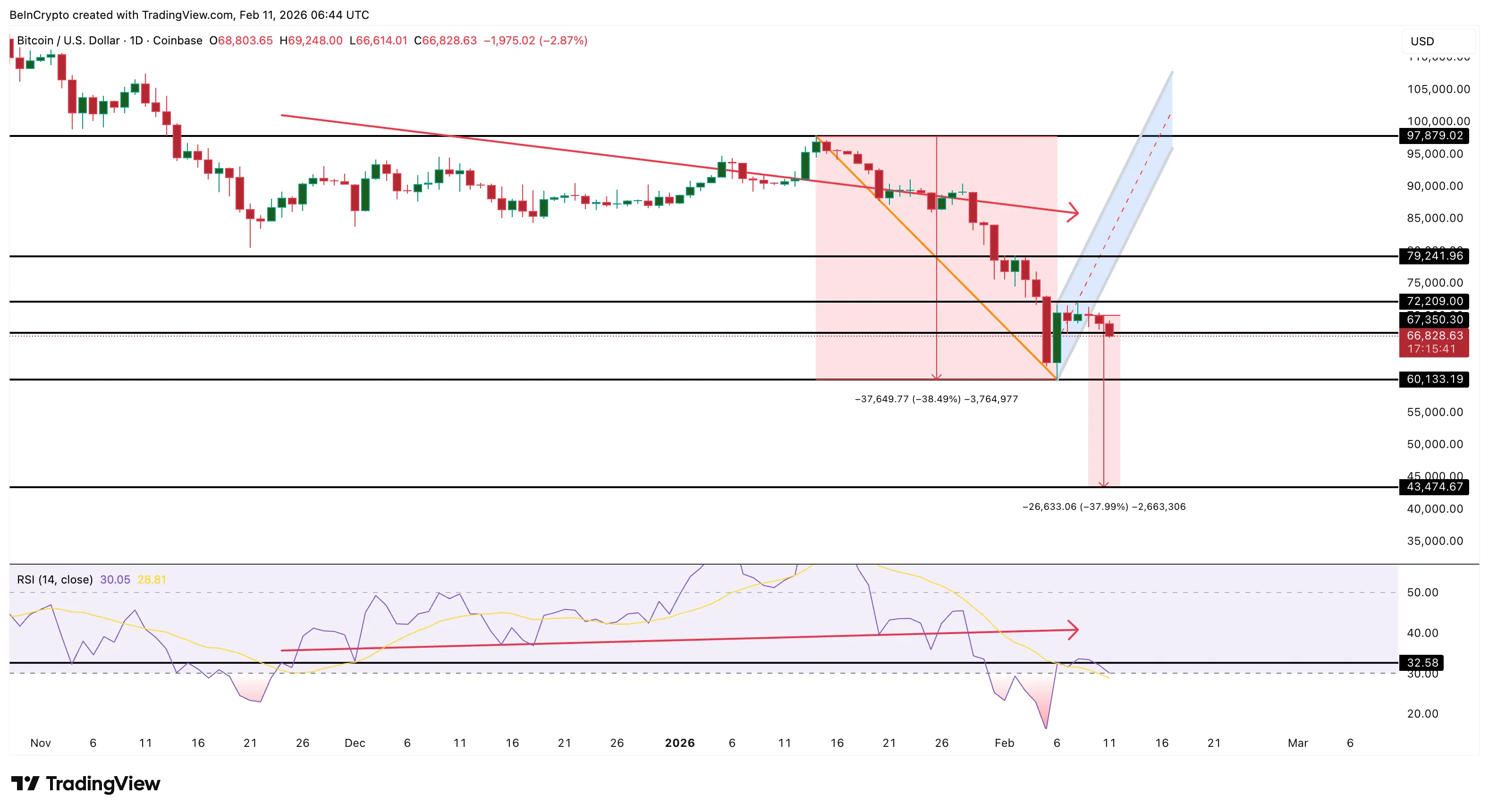
Bitcoin Price Slides After Bear Flag Failure — Is $63,000 the Last Line of Defense?
The Bitcoin price is sliding again after a failed rebound following February 6. The $BTC price is do
2026-02-11 17:02
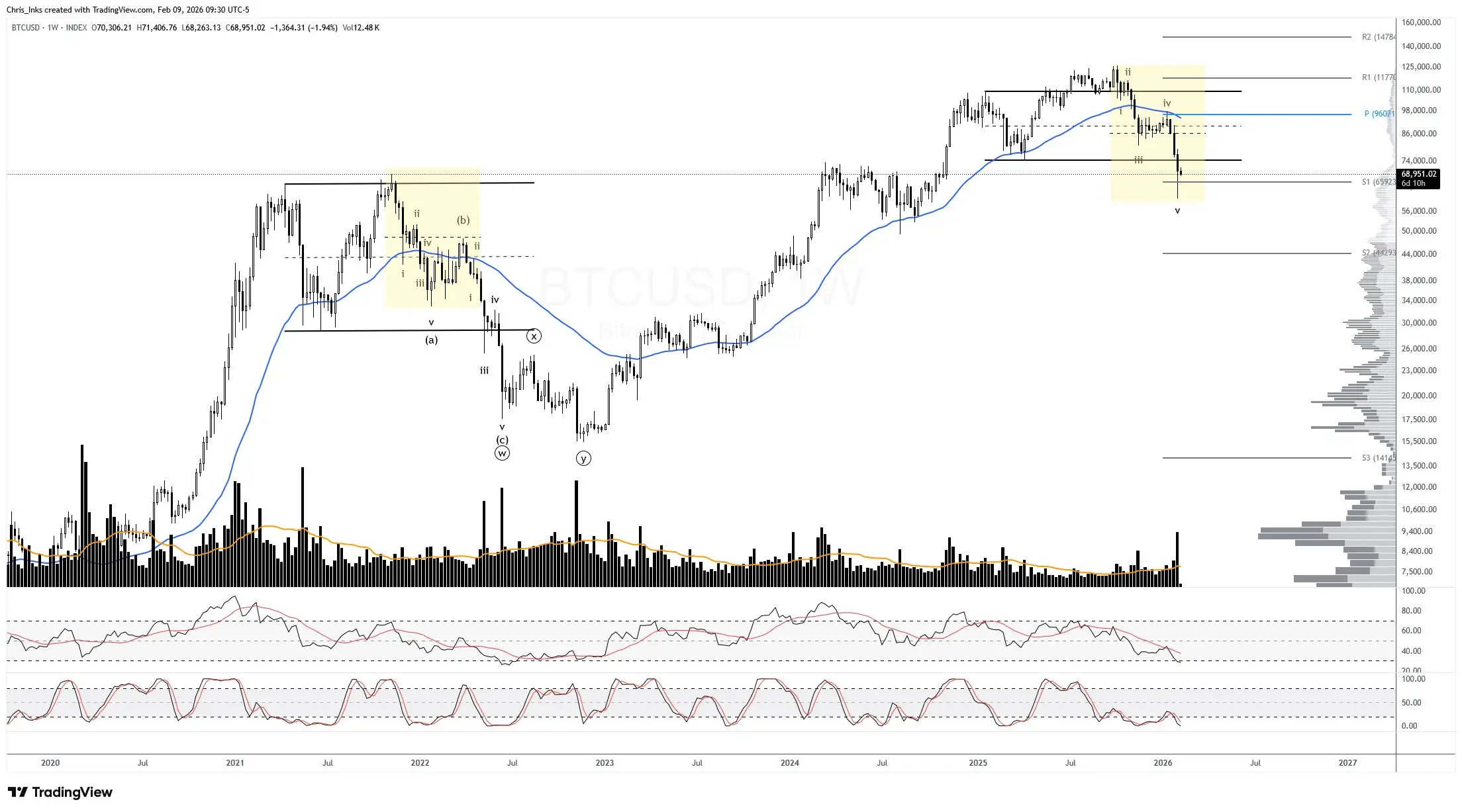
Bitcoin Chart Screams 2022 Bear Market, Until You Notice Whats Missing
Bitcoins latest drawdown from its all-time high is being compared to 2022 across crypto Twitter (the
2026-02-11 11:02
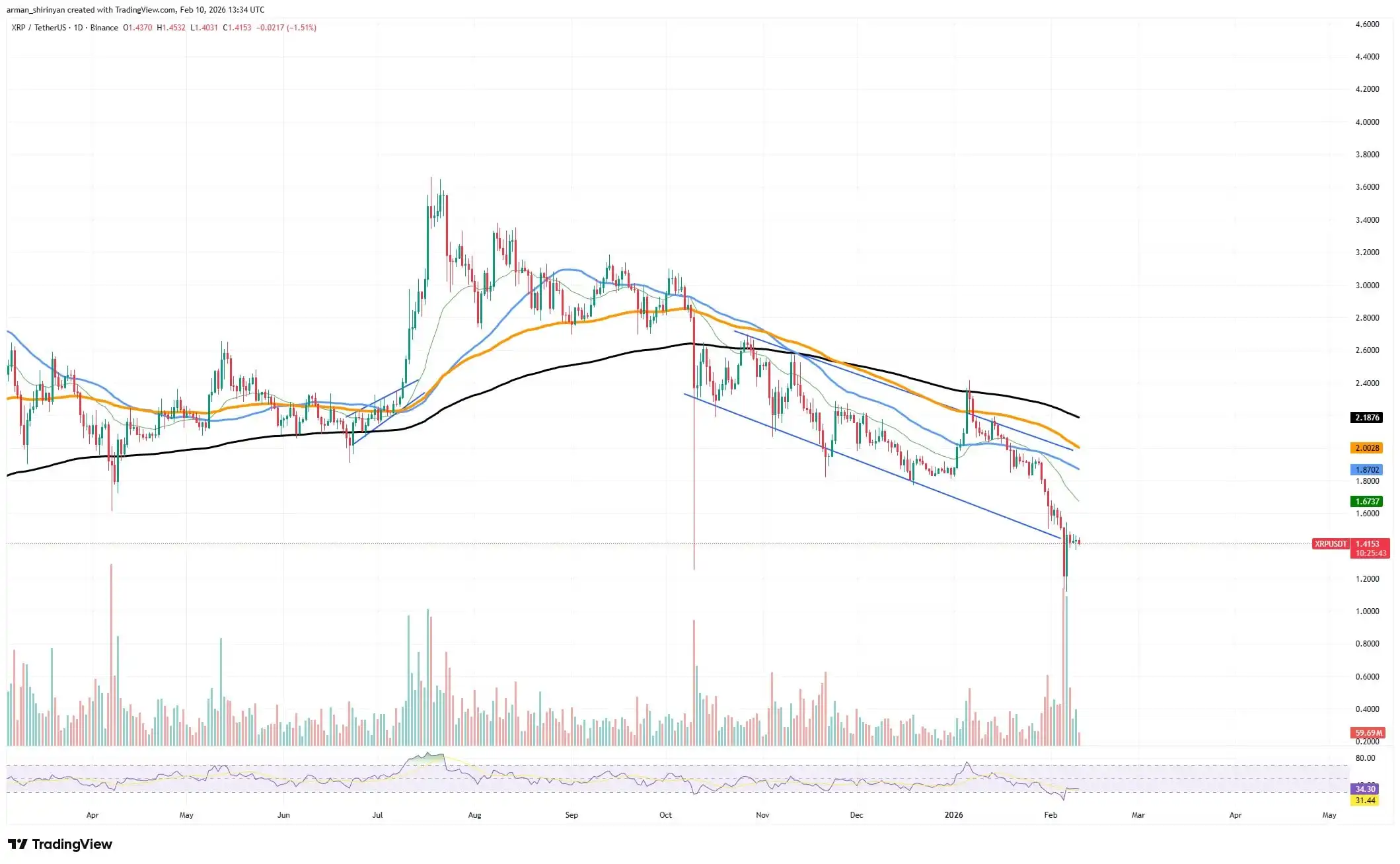
Crypto Market Review: Is XRP Actually Capitulating? Bitcoin (BTC) Eyes $64,000 Already, Shiba Inu (SHIB) Needs One More Day
The market does not appear ready for a sustained recovery, as major assets like Bitcoin, $XRP and Sh
2026-02-11 09:02
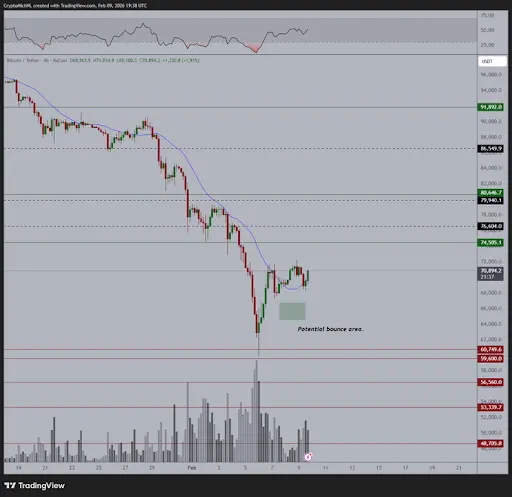
Heres Why The Bitcoin And Ethereum Prices Are Pumping Again
The Bitcoin and Ethereum prices have rebounded from last week‘s lows, providing optimism that the bo
2026-02-11 09:02

Canaan Revenue Soars in Q4 While Company Grows Its Bitcoin Treasury to Record Levels
TL;DRCanaans Q4 revenue topped $196 million, up 121% year over year, with record shipments of 14.6 e
2026-02-11 08:02
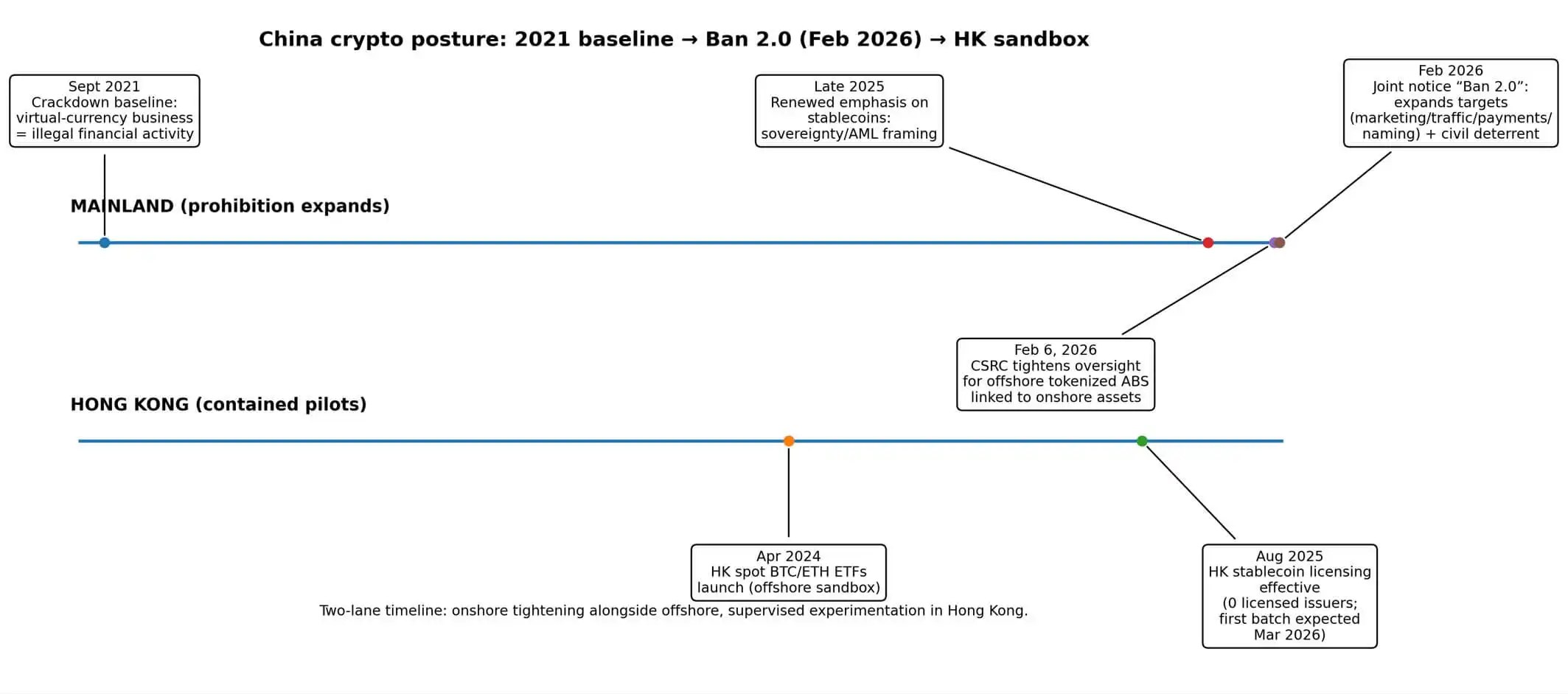
China Bitcoin legalization is priced at 5% but Beijings February 2026 Ban 2.0 made one detail brutal
Polymarket traders are pricing the prospect of China legalizing onshore Bitcoin purchases at roughly
2026-02-11 06:02